What Is Stem Cell Therapy? How It Works In 2-Minutes
Contributing Author : Gina
Big Picture
Genomic medicine is bringing hope where none previously existed. This approach to cure and treat human diseases uses human biology rather than chemical compounds made in the lab to unlock techniques and therapies with the power to cure formerly incurable diseases. The use of gene therapy, CAR T cell therapy, stem cell, and other therapies is revolutionizing medicine.
What Are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are the cells the human body uses to create differentiated cells with special functions. Some stem cells become kidney tissue. Some become lung tissue. Every cell begins as a stem cell, then goes on to specialize. Because stem cells are flexible, the body also uses them to repair systems in the body. When a fetus is forming, the stem cells are called embryonic stem cells. Adult stem cells are more commonly used in therapeutics, and in the U.S., the use of human stem cells is subject to regulation.
How Are Stem Cells Used?
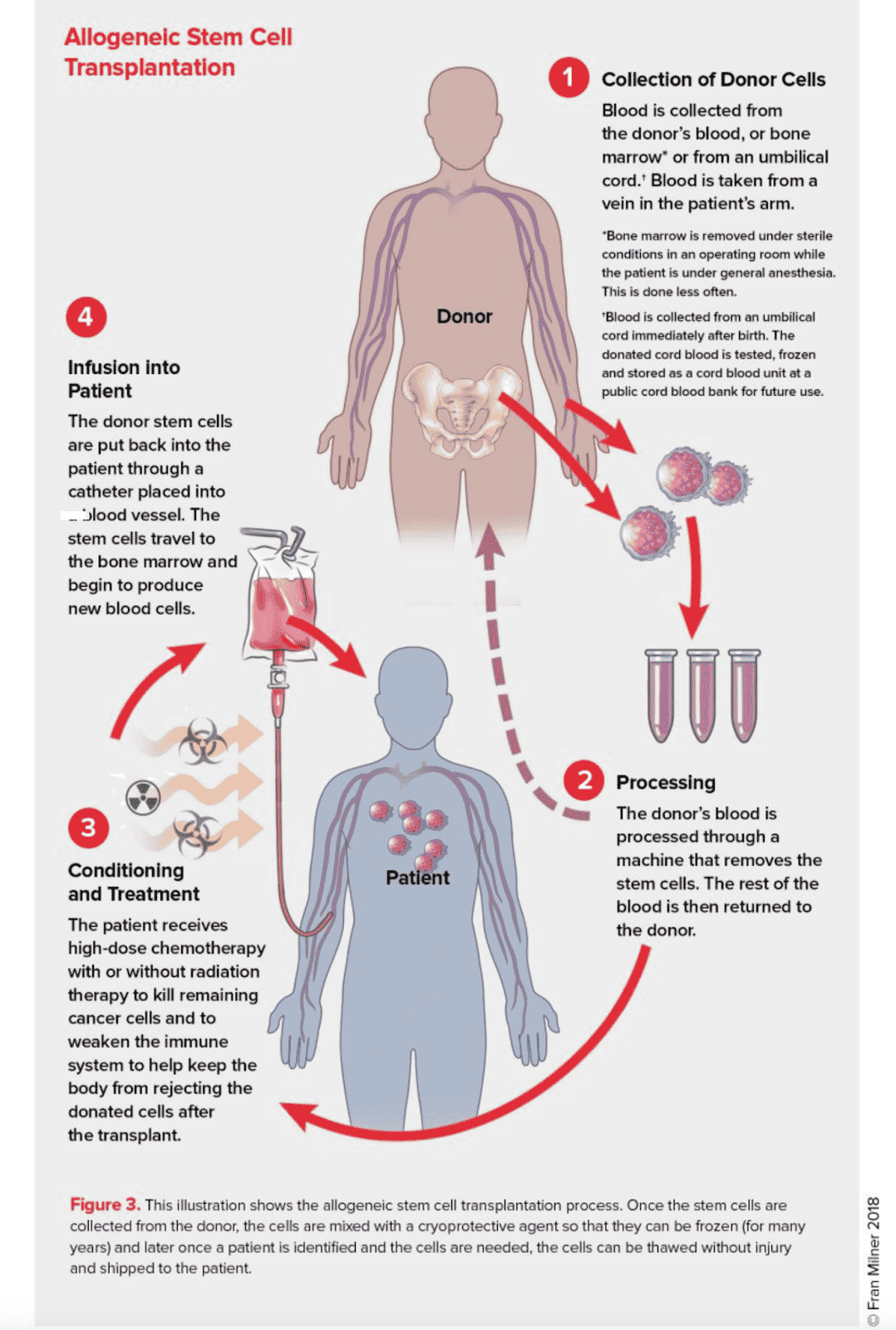
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) maintains a registry of human stem cell lines that can be used legally for research. On an individual level, stem cell (also known as bone marrow) transplants are a treatment for diseases such as leukemia. Healthy stem cells are harvested from a living donor (allogeneic cells) who is considered a match and introduced into the patient’s body during stem cell transplantation through a transfusion that is much like a blood transfusion. This is a risky procedure because the patient’s immune system must first be destroyed so that it will accept the donor stem cells. Figure 1 illustrates the stem cell transplant process.
Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Donor-to-Patient Stem Cell Transplantation
Outcome
Even when all precautions are taken, the patient’s body may reject the new stem cells, which may cause death. Patients must take an immunosuppressant for the rest of their lives to mitigate side effects and keep their bodies from rejecting these cells.1 In many stem cell therapies, the stem cells are not treated or amended in any way before they are introduced by transfusion into the patient’s body. One important note is that it is possible to save and freeze stem cells from the umbilical cord blood of newborn infants. Parents can elect to do this and may choose to do so because if those stem cells are needed in the future, they are an exact match to their child.
Learn More
What Are Stem Cells & What Can They Do?
FreeMedEd
To learn about the differences between all forms of genomic medicine watch the below video:
What’s the Difference?
American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy (ASGCT)
Sources:
1Tönshoff B. Immunosuppressants in Organ Transplantation. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2020;261:441-469. doi: 10.1007/164_2019_331. PMID: 31820175.